Human Heart.
Depending upon the mode of contraction there are two kinds of hearts:
Myogenic hearts: The hearts in which the wave of contraction starts in the muscle fibre of heart are said to be myogenic hearts. Eg. Human Heart.
Neurogenic Heart: The in which the contraction wave takes its origin from its nerve cells of group of such cells are said to be neurogenic hearts. Eg. Frog’s heart.
Structure if Human Heart.
A Human Heart is a triangular and muscular organ located in thoracic cavity between the lungs. The human heart is about 12 cm in length and 250gms in weight.
External structure of Human Heart
Human Heart is a conical muscular organ, enclosed and protected in a double chambered wall called pericardium. The cavity between two pericardial membrane s filled with pericardial fluid that prevents the heart from shocks, mechanical injury and also allows free movements of the heart.
Human Heart is a four chambered organ, having two auricles and two ventricles. Right auricles and right ventricles that deals with the impure blood whereas the left chamber is for pure blood. There is no mixing pure and impure blood inside or outside the heart.
The external structures of Human Heart are:
Auricles: Auricles are thin walled chambers. The left auricle is smaller than the right auricle, Right auricle receives impure blood from the superior venacava and inferior vanacava. Whereas the left auricle receives pure blood from the two pulmonary veins.
Ventricles: Ventricles are thick walled. The left ventricle is somewhat longer and about three times thicker than the right ventricle. Right ventricle receives impure blood from the right auricle and left ventricle receives pure blood from the left auricle.
Pulmonary trunk and aorta: The pulmonary trunk arises from the right ventricle. It divides into ledt and right pulmonary arteries that carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs. Similarly an aorta arises from the left auricle, This gives off three branches namely: Innominate, left common carotid and left subclavian.
Internal structure of Human Heart.
Auricle: Auricle are thin walled chambers separated by inter auricular septum.The opening of the venecave that provided impure blood to the right auricle is guided by Eustachian valve.
Bicuspid and tricuspid valves: The auricles and ventricles are separated by the auriculo-ventricular septum. Each auricle opens into its corresponding ventricle through an auriculo-ventriculo aperture. These apertures are guarded by flaps or valves which opens only in the ventricle and prevent the back flow of the blood . The left auriculo-ventricular aperture is guared by bicuspid valve or mitral valve. Similarly the right auricular structure is guared by tricuspid structure. These valves are attatched to the walls of the ventricles by the help of tendons of fibrous chords called chordae tendinae. Its main function is to hold the flaps.
Ventricles: Ventricles are thick walled, separated by thick and oblique inter-ventricular septum. The walls of ventricles have many muscular ridges or projections called columnae carnae. IT divides the cavity of ventricles into smaller spaces, known as fissures. Right ventricle receives the impure blood whereas the left ventricle receives pure blood. Due to the contraction of ventricles, the blood is pumped forcefully to the different parts of the body.






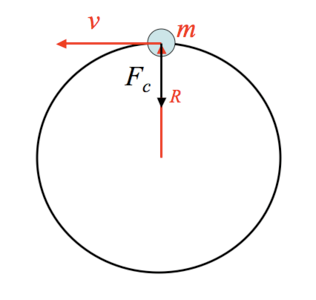
 .Now an electron can't move in a definate orbit all the time, while moving it either gains energy or looses energy. Bohr's atomic model assures that when an electron looses energy it jumps to a lower orbit and when it gains energy it jumps to a higher one.
.Now an electron can't move in a definate orbit all the time, while moving it either gains energy or looses energy. Bohr's atomic model assures that when an electron looses energy it jumps to a lower orbit and when it gains energy it jumps to a higher one.